What I've learnt about Javascript and the DOM so far...
Anahera
19 June, 2024

JavaScript and its relationship to HTML and CSS
If HTML is the structure and CSS the styling of a website, Javascript adds interactivity and dynamic functionality.
Javascript allows you to add interactive actions to a page without having to refresh. For example, at the click of a button, an accordion could open up to reveal text.
Let's imagine a bike.
HTML is the humble bicycle - the wheels, the handlebars and the brakes. It's totally functional.
CSS is the pizzaz! It's the cute basket on the front, the sparkly tassels on the handle bars and the fiery red paint (I know red makes you go faster, but in this situation it's purely cosmetic).
Javascript is the electrics, because this is no old fashioned bike - it's an e-bike! When you pedal, the motor makes you go faster. Just push a button and magic stuff happens without you having to put in a whole lot of work.
Control Flow and Loops
By default, Javascript code is executed top to bottom, line by line - similar to CSS. Control Flow allows us to control the order of execution. Loops are one way to control the flow of execution by repeating tasks when a criterion is met and doing those tasks with less code!
Imagine you have 5 plants to water. You need to repeat the action of watering each plant until you've watered all 5. Here's how a loop fits into this scenario:
- Start: Start at the first plant.
- Condition check: Check if there are more plants to water.
- If yes, proceed to water the next plant.
- If no, stop.
- Water the plant: Water the current plant.
- Continue to the next plant: Move on to the next plant.
- Repeat: Go back to the condition check and repeat the process.
The loop will continue until there are no plants left to water. Once the loop is done, then control flow would mean we continue with the next code.
Here is an example of what this would look like written the DOM using Javascript:

The DOM
The DOM (Document Object Model) allows us to interact with and manipulate HTML and CSS using Javascript.
The DOM is like an interactive version of an HTML document. Our browsers use the DOM to show what's on the webpage, so when you make changes to the DOM, the page updates instantly. Despite those changes, the original HTML file will stay the same unless you manually change and reload it.
To use an analogy, imagine two bedrooms with identical furniture - the same bed, drawers, bedside tables, lamps and a mirror. One bedroom is the HTML, representing the initial set up and structure. The second is the DOM bedroom, a live and interactive version.
The DOM bedroom lets you move furniture around, repaint the walls, or add new decorations when you want. You'll see all of your changes instantly just as it works to the DOM webpage without needing to reload it.
While no changes are made to the HTML bedroom and it stays the same, unaffected by the DOM.
The DOM has a slightly different interface from what we're used to with HTML. The DOM takes the HTML and formats it into a tree structure. And all the HTML elements that exist can be selected as objects in the DOM.
With the DOM, you can select objects (like paragraph text) on a page, use methods to listen for events (like clicks) relating to that object, or add properties to the element (like change its background colour).
Example
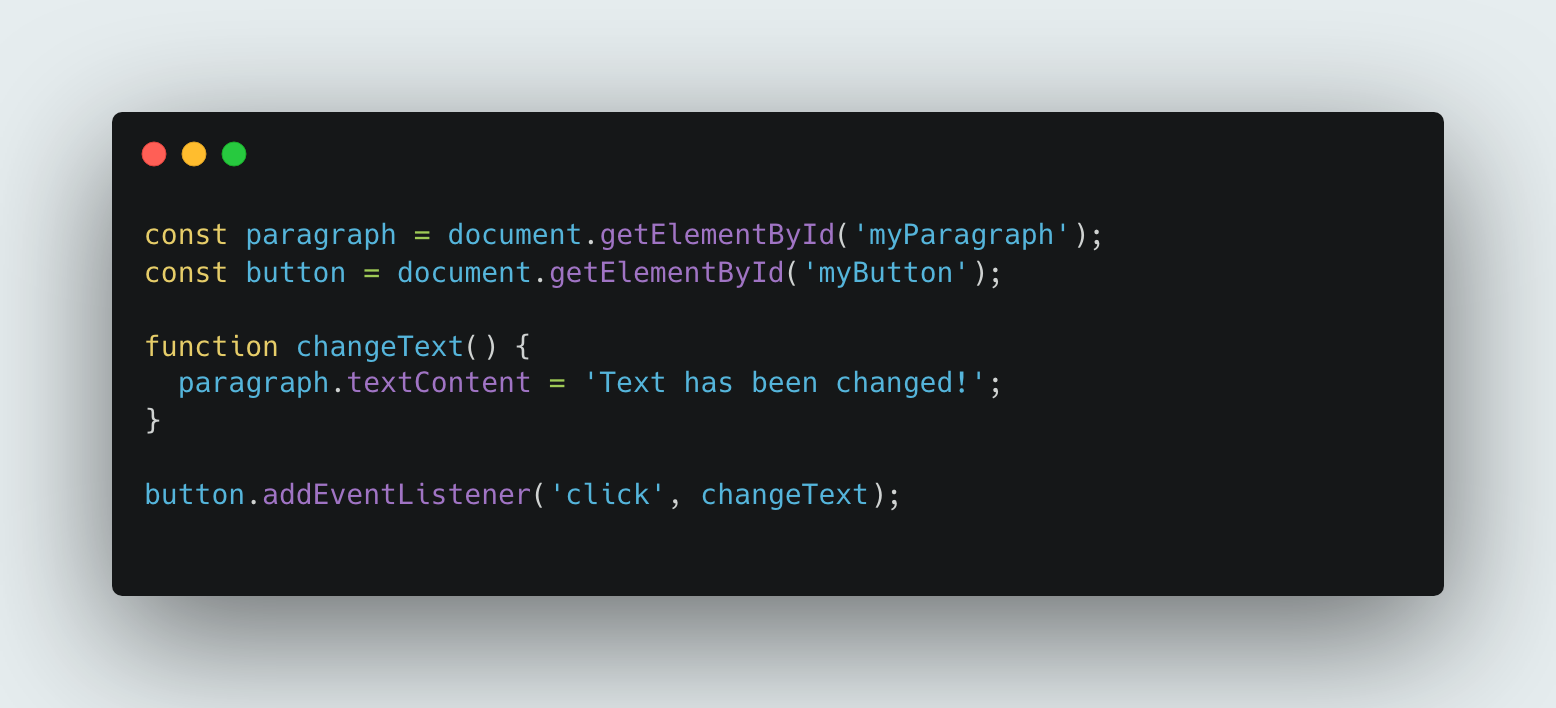
The following example selects the elements, defines a function that changes the text of the paragraph and thn adds an event listener to the button that calls the the changeText function when clicked.
The difference between accessing data from arrays and objects
Arrays and objects are both data structures that you can choose from depending on the situation.
Arrays are a group of indexed items that you can call on using their position in the group using "array[index]". You would usually use arrays for items where the order matters e.g. lists, timelines, series of numbers, group of names, etc.
Objects can be used to store data that can be identified by a name rather than position and you can call them using "object.key" or "object[key]".Objects are best for collections of key-value pairs such as contact information, product info, words and their definitions, etc.
An key difference between the two is the importance of indexing the positions, arrays do this and objects do not.
What the heck does "key-value pair" mean?
The term "key-value pair" is used to desribe a set of two linked data items.
e.g. Age: 30;
'Age' would be the key, '30' would be the value.
When you want to know the number of years, you look up 'Age' and find its value.
Functions
Functions are code that perform specific tasks. A function performs when it is called, such as clicking a button, or as part of the default control flow.
What's great about them is that they are reusable and you can call on them whenever you like and without having to rewrite the same code.
Some kinda call to action copy goes here.